Inside the Neural Vocoder Zoo: WaveNet to Diffusion in Four Audio Clips
Hey everyone, I’m Oleh Datskiv, Lead AI Engineer at the R&D Data Unit of N-iX. Lately, I’ve been working on text-to-speech systems and, more specifically, on the unsung hero behind them: the neural vocoder.
Let me introduce you to this final step of the TTS pipeline — the part that turns abstract spectrograms into the natural-sounding speech we hear.
Introduction
If you’ve worked with text‑to‑speech in the past few years, you’ve used a vocoder - even if you didn’t notice it. The neural vocoder is the final model in the Text to Speech (TTS) pipeline; it turns a mel‑spectrogram into the sound you can actually hear.
Since the release of WaveNet in 2016, neural vocoders have evolved rapidly. They become faster, lighter, and more natural-sounding. From flow-based to GANs to diffusion, each new approach has pushed the field closer to real-time, high-fidelity speech.
2024 felt like a definitive turning point: diffusion-based vocoders like FastDiff were finally fast enough to be considered for real-time usage, not just batch synthesis as before. That opened up a range of new possibilities. The most notable ones were smarter dubbing pipelines, higher-quality virtual voices, and more expressive assistants, even if you’re not utilizing a high-end GPU cluster.
But with so many options that we now have, the questions remain:
- How do these models sound side-by-side?
- Which ones keep latency low enough for live or interactive use?
- What is the best choice of a vocoder for you?
This post will examine four key vocoders: WaveNet, WaveGlow, HiFi‑GAN, and FastDiff. We’ll explain how each model works and what makes them different. Most importantly, we’ll let you hear the results of their work so you can decide which one you like better. Also, we will share custom benchmarks of model evaluation that were done through our research.
What Is a Neural Vocoder?
At a high level, every modern TTS system still follows the same basic path:
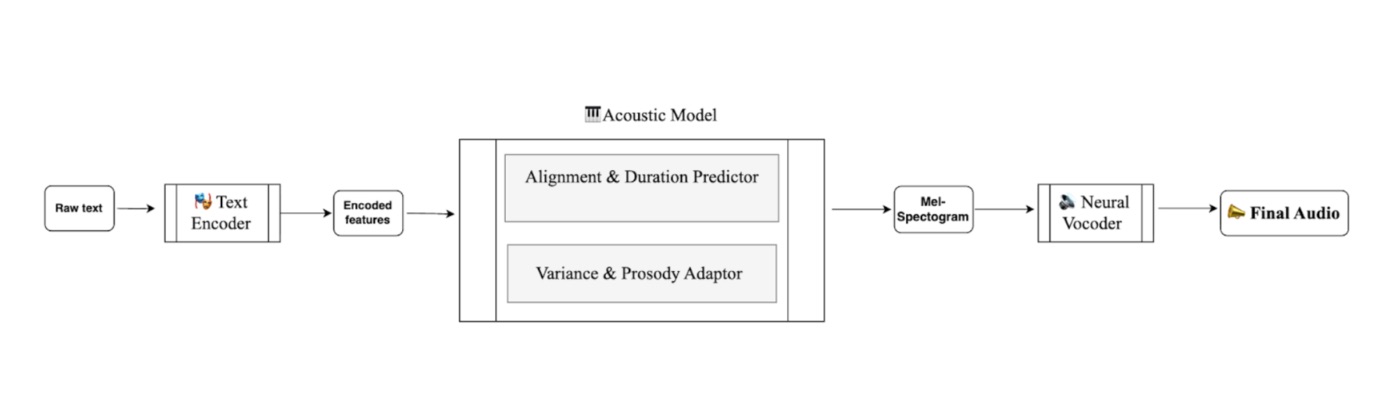
\ Let’s quickly go over what each of these blocks does and why we are focusing on the vocoder today:
- Text encoder: It changes raw text or phonemes into detailed linguistic embeddings.
- Acoustic model: This stage predicts how the speech should sound over time. It turns linguistic embeddings into mel spectrograms that show timing, melody, and expression. It has two critical sub-components:
- Alignment & duration predictor: This component determines how long each phoneme should last, ensuring the rhythm of speech feels natural and human
- Variance/prosody adaptor: At this stage, the adaptor injects pitch, energy, and style, shaping the melody, emphasis, and emotional contour of the sentence.
- Neural vocoder: Finally, this model converts the prosody-rich mel spectrogram into actual sound, the waveform we can hear.
The vocoder is where good pipelines live or die. Map mels to waveforms perfectly, and the result is a studio-grade actor. Get it wrong, and even with the best acoustic model, you will get metallic buzz in the generated audio. That’s why choosing the right vocoder matters - because they’re not all built the same. Some optimize for speed, others for quality. The best models balance naturalness, speed, and clarity.
The Vocoder Lineup
Now, let's meet our four contenders. Each represents a different generation of neural speech synthesis, with its unique approach to balancing the trade-offs between audio quality, speed, and model size. The numbers below are drawn from the original papers. Thus, the actual performance will vary depending on your hardware and batch size. We will share our benchmark numbers later in the article for a real‑world check.
- WaveNet (2016): The original fidelity benchmark
Google's WaveNet was a landmark that redefined audio quality for TTS. As an autoregressive model, it generates audio one sample at a time, with each new sample conditioned on all previous ones. This process resulted in unprecedented naturalness at the time (MOS=4.21), setting a "gold standard" that researchers still benchmark against today. However, this sample-by-sample approach also makes WaveNet painfully slow, restricting its use to offline studio work rather than live applications.
- WaveGlow (2019): Leap to parallel synthesis
To solve WaveNet's critical speed problem, NVIDIA's WaveGlow introduced a flow-based, non-autoregressive architecture. Generating the entire waveform in a single forward pass drastically reduced inference time to approximately 0.04 RTF, making it much faster than in real time. While the quality is excellent (MOS≈3.961), it was considered a slight step down from WaveNet's fidelity. Its primary limitations are a larger memory footprint and a tendency to produce a subtle high-frequency hiss, especially with noisy training data.
- HiFi-GAN (2020): Champion of efficiency
HiFi-GAN marked a breakthrough in efficiency using a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) with a clever multi-period discriminator. This architecture allows it to produce extremely high-fidelity audio (MOS=4.36), which is competitive with WaveNet, but is fast from a remarkably small model (13.92 MB). It's ultra-fast on a GPU (<0.006×RTF) and can even achieve real-time performance on a CPU, which is why HiFi-GAN quickly became the default choice for production systems like chatbots, game engines, and virtual assistants.
- FastDiff (2025): Diffusion quality at real-time speed
Proving that diffusion models don't have to be slow, FastDiff represents the current state-of-the-art in balancing quality and speed. Pruning the reverse diffusion process to as few as four steps achieves top-tier audio quality (MOS=4.28) while maintaining fast speeds for interactive use (~0.02×RTF on a GPU). This combination makes it one of the first diffusion-based vocoders viable for high-quality, real-time speech synthesis, opening the door for more expressive and responsive applications.
Each of these models reflects a significant shift in vocoder design. Now that we've seen how they work on paper, it's time to put them to the test with our own benchmarks and audio comparisons.
\n Let’s Hear It — A/B Audio Gallery
Nothing beats your ears!
We will use the following sentences from the LJ Speech Dataset to test our vocoders. Later in the article, you can also listen to the original audio recording and compare it with the generated one.
Sentences:
- “A medical practitioner charged with doing to death persons who relied upon his professional skill.”
- “Nothing more was heard of the affair, although the lady declared that she had never instructed Fauntleroy to sell.”
- “Under the new rule, visitors were not allowed to pass into the interior of the prison, but were detained between the grating.”
The metrics we will use to evaluate the model’s results are listed below. These include both objective and subjective metrics:
- Naturalness (MOS): How human-like does it sound (rated by real people on a 1/5 scale)
- Clarity (PESQ / STOI): Objective scores that help measure intelligibility and noise/artifacts. The higher, the better.
- Speed (RTF): An RTF of 1 means it takes 1 second to generate 1 second of audio. For anything interactive, you’ll want this at 1 or below
Audio Players
(Grab headphones and tap the buttons to hear each model.)
| Sentence | Ground truth | WaveNet | WaveGlow | HiFi‑GAN | FastDiff | |----|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:| | S1 | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | | S2 | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | | S3 | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ | ▶️ |
\n Quick‑Look Metrics
Here, we will show you the results obtained for the models we evaluate.
| Model | RTF ↓ | MOS ↑ | PESQ ↑ | STOI ↑ | |----|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:| | WaveNet | 1.24 | 3.4 | 1.0590 | 0.1616 | | WaveGlow | 0.058 | 3.7 | 1.0853 | 0.1769 | | HiFi‑GAN | 0.072 | 3.9 | 1.098 | 0.186 | | FastDiff | 0.081 | 4.0 | 1.131 | 0.19 |
\n *For the MOS evaluation, we used voices from 150 participants with no background in music.
** As an acoustic model, we used Tacotron2 for WaveNet and WaveGlow, and FastSpeech2 for HiFi‑GAN and FastDiff.
\n Bottom line
Our journey through the vocoder zoo shows that while the gap between speed and quality is shrinking, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Your choice of a vocoder in 2025 and beyond should primarily depend on your project's needs and technical requirements, including:
- Runtime constraints (Is it an offline generation or a live, interactive application?)
- Quality requirements (What’s a higher priority: raw speed or maximum fidelity?)
- Deployment targets (Will it run on a powerful cloud GPU, a local CPU, or a mobile device?)
As the field progresses, the lines between these choices will continue to blur, paving the way for universally accessible, high-fidelity speech that is heard and felt.
You May Also Like

Republic Europe Offers Indirect Kraken Stake via SPV

cpwrt Limited Positions Customer Support as a Strategic Growth Function
