Evaluating Novel 3D Semantic Instance Map for Vision-Language Navigation
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
-
Related Works
2.1. Vision-and-Language Navigation
2.2. Semantic Scene Understanding and Instance Segmentation
2.3. 3D Scene Reconstruction
-
Methodology
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Open-set Semantic Information from Images
3.3. Creating the Open-set 3D Representation
3.4. Language-Guided Navigation
-
Experiments
4.1. Quantitative Evaluation
4.2. Qualitative Results
-
Conclusion and Future Work, Disclosure statement, and References
4. Experiments
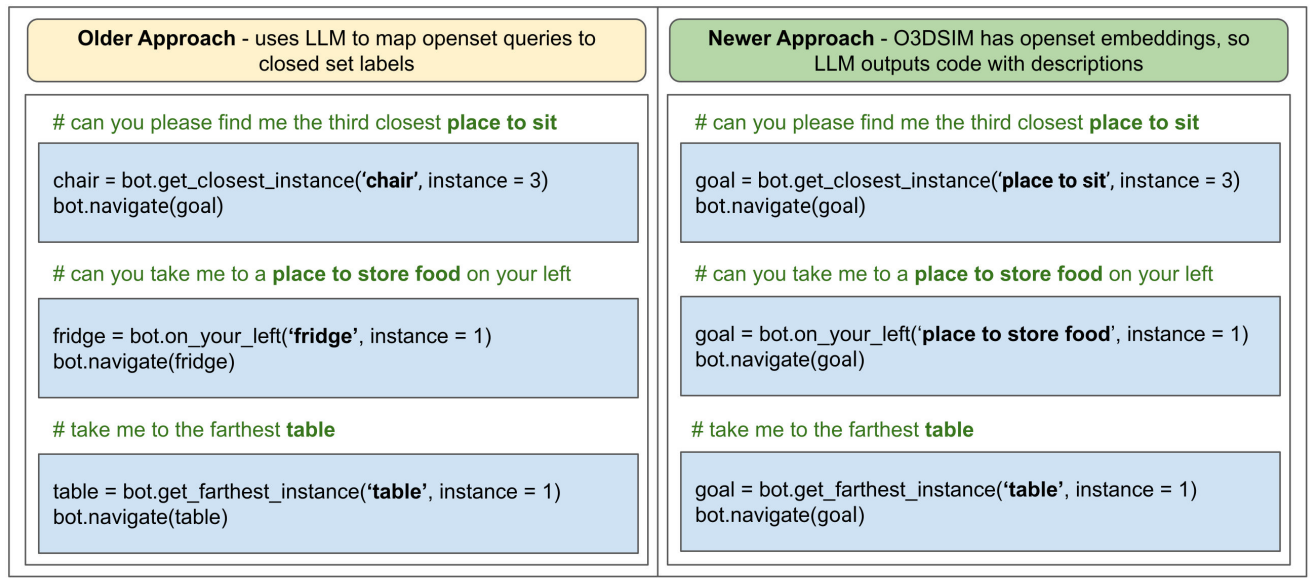
Having introduced the O3D-SIM creation pipeline and its integration with ChatGPT for natural language understanding and Vision-Language Navigation (VLN) enhancement, we now turn to the evaluation of this novel representation both quantitatively and qualitatively. This will also shed light on the impact of the O3D-SIM representation on an agent’s ability to execute queries that mimic human interaction. The evaluation is structured into two subsections: Section 4.1 focuses on the quantitative assessment of O3D-SIM, and Section 4.2 addresses the qualitative analysis of the representation.
\ 
\
:::info Authors:
(1) Laksh Nanwani, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India; this author contributed equally to this work;
(2) Kumaraditya Gupta, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India;
(3) Aditya Mathur, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India; this author contributed equally to this work;
(4) Swayam Agrawal, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India;
(5) A.H. Abdul Hafez, Hasan Kalyoncu University, Sahinbey, Gaziantep, Turkey;
(6) K. Madhava Krishna, International Institute of Information Technology, Hyderabad, India.
:::
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC by-SA 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Sharealike 4.0 International) license.
:::
\
Ayrıca Şunları da Beğenebilirsiniz

USD/CAD rises above 1.3750 after rebounding from three-month lows

US Government Taps Coinbase, Robinhood for Tech Talent in New Initiative
